Innovation is the lifeblood of progress—whether you’re a solo creator or leading a Fortune 500 team, understanding how breakthroughs happen can transform your creative output. In this comprehensive guide to the psychology of innovation, we’ll unveil ten timeless techniques that tap into the neuroscience of creativity, cultivate an innovative mindset, and sustain unstoppable creative flow.
The Psychology Behind Innovation And Creative Flow
At the core of every groundbreaking idea lies a rich interplay between mind and brain. In this section, we’ll define innovation psychology, explore the neuroscience of creativity, and identify the key drivers that fuel an unstoppable creative flow. Armed with these insights, you’ll gain a deeper appreciation for how thought patterns, neural networks, and motivational forces converge to spark true innovation.
Defining Innovation Psychology And Its Impact
Innovation psychology examines the cognitive and emotional processes that underpin creative problem‑solving and idea generation. By studying factors such as mindset, motivation, and perception, this discipline reveals why some individuals consistently produce novel concepts while others struggle to break free from conventional thinking.
- Innovative Mindset: A belief that abilities can grow through effort, embracing challenges and persisting through setbacks.
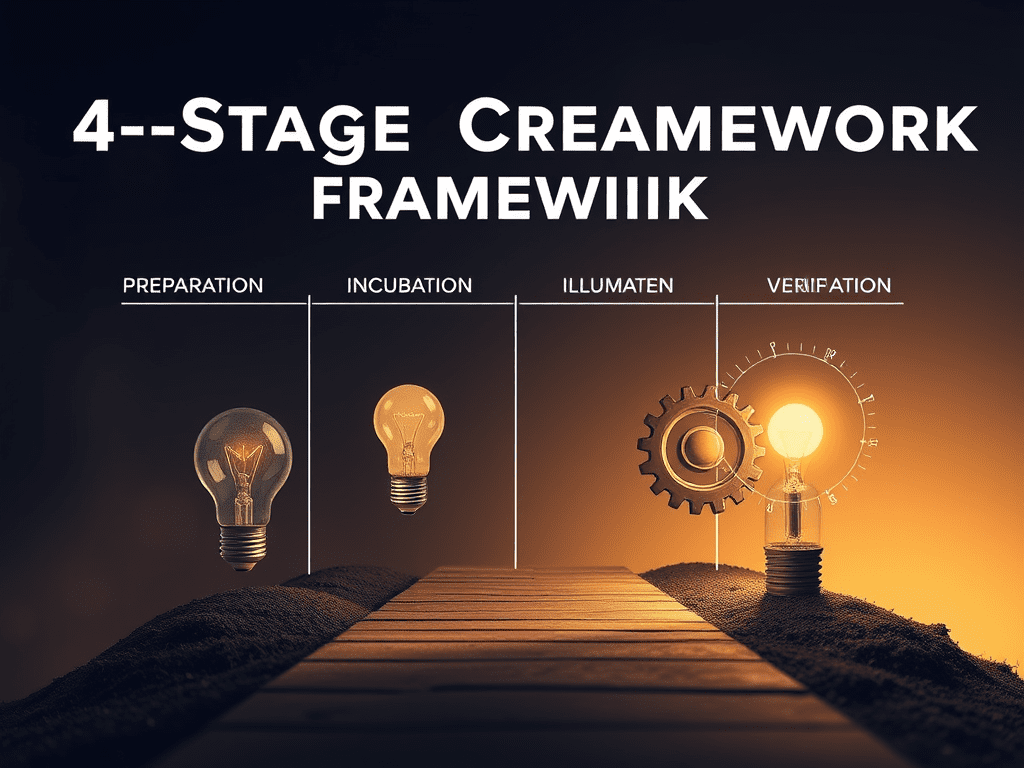
- Creative Process: A non‑linear journey involving preparation, incubation, illumination, and verification phases.
- Psychological Safety: Feeling secure enough to take risks without fear of judgment—essential for candid brainstorming and experimentation.
By understanding these core components, organizations can design environments and routines that amplify curiosity, resilience, and collaborative synergy—laying the groundwork for innovation to flourish.
Exploring The Neuroscience Of Creativity
Behind every “aha!” moment is a dynamic dance between distinct brain networks. Recent research into the neuroscience of creativity highlights how connectivity patterns and neurochemicals shape our capacity for creative flow:
- Default Mode Network (DMN): Engages during mind‑wandering and free association, fueling the generation of novel ideas.
- Executive Control Network (ECN): Manages focus and critical evaluation, ensuring ideas are refined and practical.
- Salience Network: Detects meaningful stimuli, facilitating seamless switching between divergent thinking and focused problem‑solving.
- Dopamine Pathways: Reward circuits that reinforce creative behaviors, boosting motivation to explore new concepts.
When these networks synchronize—often in a flow state—creativity surges, enabling fast idea generation coupled with disciplined refinement. Understanding how your brain toggles between spontaneous and critical modes empowers you to structure work sessions that maximize creative flow.
Key Drivers Of Unstoppable Creative Flow
While brain networks set the stage, certain psychological drivers propel innovation from seedling to breakthrough. Cultivating these forces in your personal routine and team culture will sustain an unstoppable creative flow:
- Intrinsic Motivation: Passion‑driven projects spark deeper engagement and more original solutions than extrinsic rewards alone.
- Autonomy: Freedom to choose methods and directions encourages ownership and experimental risk‑taking.
- Challenge Balance: Tasks should stretch skills just enough to avoid boredom or overwhelm—landing in the optimal zone for flow.
- Domain Expertise: A robust knowledge base provides raw materials for novel combinations, enhancing divergent thinking.
- Psychological Safety: A culture where mistakes are viewed as learning opportunities, not failures, accelerates iteration.
- Environmental Cues: Spaces that inspire—through color, layout, or tools—can prime the mind for creative work.
By intentionally designing your mindset and environment around these drivers, you activate the full power of the psychology of innovation. In the next sections, we’ll dive into ten actionable techniques—ranging from growth mindset exercises to collaborative rituals—that leverage these scientific insights and catalyze your most prolific creative flow yet.
Technique 1: Cultivating A Growth Mindset For Breakthrough Ideas
Developing a growth mindset is the foundation for unlocking your highest creative potential. By reframing challenges as opportunities and embracing continuous learning, you prime your brain to generate breakthrough ideas and sustain an unstoppable creative flow. In this section, we’ll contrast fixed and growth mindsets, then explore practical exercises—like daily affirmations and resilience training—that rewire your innovation psychology for long‑term success.
Understanding Growth Mindset Versus Fixed Mindset
Psychologist Carol Dweck’s landmark research differentiates two core mindsets:
- Fixed Mindset: Belief that talent and intelligence are static traits. Individuals with a fixed mindset often avoid challenges, give up easily when faced with setbacks, and view effort as fruitless.
- Growth Mindset: Conviction that abilities can be developed through dedication and hard work. Growth‑oriented innovators embrace obstacles, persist through failure, and see effort as the path to mastery.
In the context of innovation psychology, a growth mindset acts as the engine for creative flow. When you view every problem as an opportunity to learn, your brain releases dopamine—fueling motivation and sharpening focus. Over time, this neurochemical reinforcement makes resilience and experimentation habitual, accelerating breakthrough thinking.
Practical Exercises To Rewire Your Innovation Mindset
Transforming deeply held beliefs requires deliberate practice. Below are two high‑impact exercises designed to rewire your cognitive patterns and embed a lasting growth mindset.
Daily Affirmations And Cognitive Reframing
- Create Positive Scripts: Each morning, write or speak three affirmations that reinforce growth beliefs—for example, “I improve with every challenge” or “Failures are fuel for my creativity.”
- Reframe Negative Thoughts: When you catch yourself thinking “I can’t do this,” immediately counter with “What can I learn from this setback?” This habit shifts your internal dialogue from defeatist to solution‑oriented.
- Visualization Techniques: Spend two minutes visualizing past challenges you overcame. Recall the strategies you used and the satisfaction of succeeding despite obstacles. This primes your neural networks for perseverance.
Consistent practice of affirmations and reframing rewires neural pathways, fostering stronger connections in the prefrontal cortex—essential for adaptive thinking and sustained creative flow.
Learning From Failure And Resilience Training
- Failure Journaling: After any setback, document what went wrong, what you learned, and how you’ll apply those lessons. This reflective exercise converts negative experiences into actionable insights.
- Resilience Drills: Periodically expose yourself to controlled challenges—like learning a new skill under time pressure or tackling a mini‑innovation sprint. Overcoming these “safe failures” builds confidence for larger creative risks.
- Peer Feedback Cycles: Share early‑stage ideas with a trusted colleague or mastermind group. Solicit candid feedback, then iterate based on insights. Embracing critique without defensiveness strengthens psychological safety and collaborative innovation.
By systematically analyzing failures and embedding resilience drills into your routine, you cultivate mental toughness. This toughness acts as a catalyst for creative breakthroughs, enabling you to pivot quickly, iterate boldly, and transform setbacks into stepping stones.
Mastering a growth mindset doesn’t happen overnight—it’s an ongoing discipline. But by integrating daily affirmations, cognitive reframing, failure journaling, and resilience training into your workflow, you build the mental architecture needed for uninterrupted creative flow. Up next, we’ll explore how divergent thinking tools amplify those growth mindset foundations to spark an abundance of novel concepts.
Technique 2: Embracing Divergent Thinking To Spark Novel Concepts
Divergent thinking is the engine that propels innovation beyond obvious solutions. By intentionally expanding your idea horizons and leveraging varied tools, you open pathways to unexpected connections and breakthrough concepts. In this section, we’ll explore proven methods for divergent idea generation and dive into brainstorming techniques—complete with mind mapping and the SCAMPER framework—to amplify creative flow and cultivate a wealth of novel insights.
Tools And Methods For Divergent Idea Generation
Divergent thinking thrives when you have the right cognitive tools at your disposal. Below are high‑leverage methods to spark an abundance of ideas:
- Lateral Thinking Puzzles: Tackle brainteasers that force you to abandon linear reasoning and discover unconventional solutions.
- Analogy Mapping: Draw parallels between unrelated domains (e.g., nature and technology) to transfer insights across fields and inspire fresh concepts.
- Forced Connections: Randomly select two disparate objects or ideas and brainstorm ways they might intersect—this jostles your neural networks into new pattern recognitions.
- Random Stimulus Technique: Use a deck of random images, words, or sounds as prompts. Jot down any associations that emerge, then refine the most intriguing ones.
- Attribute Listing: Break down a problem into its core attributes (e.g., speed, size, cost) and ideate adjustments to each attribute independently.
Integrating these tools into your innovation practice ensures that your mind doesn’t default to habitual thought patterns. Instead, you actively cultivate flexibility—an essential ingredient for an unstoppable creative flow.
Brainstorming Techniques To Expand Idea Horizons
Brainstorming remains one of the most accessible strategies for harnessing divergent thinking. To maximize its effectiveness, structure your sessions with these best‑practice techniques:
- Traditional Brainstorming: Gather a small, diverse group, set a clear challenge, and encourage rapid-fire idea generation without judgment or critique.
- Brainwriting: Participants write three to five ideas on paper, then pass it to the next person to build upon—this avoids groupthink and ensures quieter voices are heard.
- Round‑Robin Brainstorming: Each person contributes one idea in turn, fostering equal participation and preventing dominant personalities from monopolizing the session.
- Question Storming: Instead of proposing solutions, generate as many questions as possible about the problem space, then invert questions into potential ideas.
- Six Thinking Hats: Adopt Edward de Bono’s framework by assigning different “hats” (e.g., optimistic, critical, creative) to team members, ensuring balanced exploration of pros, cons, and alternatives.
Mind Mapping As A Creativity Hack
- Central Theme: Write the core problem or goal in the center of a whiteboard or digital canvas.
- Branching Ideas: Draw branches for each major subtopic or category, then add secondary and tertiary nodes for details and associations.
- Visual Cues: Use colors, icons, and images to differentiate branches, engaging both hemispheres of your brain and reinforcing memory.
- Iterative Expansion: After the initial pass, revisit each branch to generate second‑order connections—look for cross‑links between nonadjacent nodes.
- Digital Tools: Leverage software like XMind or MindMeister for collaborative mapping, version control, and easy rearrangement of ideas.
SCAMPER Method For Continuous Improvement
- Substitute: Replace one component or process with another—e.g., substitute physical brochures with an interactive app.
- Combine: Merge two or more ideas or functions—e.g., combine social media live‑streaming with real‑time customer feedback.
- Adapt: Modify an existing solution to serve a new purpose—e.g., adapt gaming mechanics to employee training modules.
- Modify (Magnify/Minify): Change scale or form—e.g., micro‑learning modules instead of hour‑long workshops.
- Put to Other Uses: Apply your idea in a different context—e.g., use drone delivery concepts for medical supply distribution.
- Eliminate: Remove unnecessary elements to streamline—e.g., eliminate redundant approval steps in project workflows.
- Reverse/Rearrange: Flip the sequence or perspective—e.g., reverse the user journey to identify hidden pain points.
By cycling through SCAMPER questions, you ensure continuous refinement of concepts, preventing stagnation and fuelling an enduring creative flow.
Mastering divergent thinking techniques is pivotal for generating a wealth of novel concepts. With these tools and structured brainstorming approaches—like mind mapping and SCAMPER—you’ll consistently produce breakthrough ideas. Next, we’ll explore advanced innovation methods that integrate design thinking, mindfulness, and systems thinking to further supercharge your creative flow.
Techniques 3–5: Advanced Innovation Methods To Supercharge Creativity
Having established a growth mindset and mastered divergent thinking, it’s time to elevate your innovation practice with advanced methods. Techniques 3 through 5—design thinking, mindfulness paired with flow states, and systems thinking—offer powerful frameworks to refine, focus, and scale your most disruptive ideas. These approaches integrate human‑centered design, neuropsychological insights, and holistic problem‑solving to sustain peak creative performance.
Technique 3: Integrating Design Thinking Principles
Design thinking is a structured, empathy‑driven approach to innovation that balances desirability, feasibility, and viability. By following its iterative stages, you cultivate solutions that resonate deeply with end users while maintaining creative flow.
Empathy Mapping For User‑Centered Solutions
- Gather Qualitative Insights: Conduct interviews, observe users, and collect stories to understand pains, gains, and daily routines.
- Build Empathy Maps: Chart what users say, think, feel, and do. This visual tool highlights hidden needs and emotional triggers.
- Identify Design Opportunities: Use empathy findings to pinpoint underserved pain points—fueling targeted brainstorming sessions.
Rapid Prototyping To Accelerate Iteration
- Low‑Fidelity Models: Sketch wireframes or create paper prototypes to externalize ideas quickly and cheaply.
- User Feedback Loops: Test early prototypes with real users, capturing reactions, suggestions, and usability data.
- Iterate Fast: Refine prototypes based on feedback, then retest. Short cycles of build‑measure‑learn keep creative momentum high.
Technique 4: Leveraging Mindfulness And Flow States
Mindfulness techniques prime the brain for deep focus, while flow states unlock heightened creativity. Together, they form a dual‑track strategy to supercharge ideation and execution.
Guided Meditation For Creative Clarity
- Focused Attention Practice: Spend 5–10 minutes daily on breath awareness to reduce noise in the prefrontal cortex and enhance idea generation.
- Open Monitoring Meditation: Observe thoughts and sensations non‑judgmentally, cultivating a receptive mental environment for novel insights.
- Visualization Sessions: Combine guided imagery with specific innovation goals—imagining successful prototypes or breakthrough scenarios to reinforce neural pathways.
Time‑Boxing And Focused Work Intervals
- Pomodoro Technique: Alternate 25‑minute deep‑work sprints with 5‑minute breaks to maintain sustained concentration and prevent mental fatigue.
- Mono‑Tasking Rules: Disable notifications and eliminate multitasking to ensure uninterrupted flow during critical ideation phases.
- Environmental Cues: Use sensory triggers—such as a specific playlist or workspace lighting—to signal the brain that it’s time for deep creative work.
Technique 5: Adopting Systems Thinking To Connect The Dots
Systems thinking expands your perspective from individual components to the relationships and feedback loops that define complex challenges. This holistic lens uncovers leverage points for transformative innovation.
Mapping Interdependencies In Complex Problems
- Causal Loop Diagrams: Illustrate how variables influence each other, revealing reinforcing and balancing loops that drive system behavior.
- Stock‑Flow Models: Distinguish accumulations (stocks) from activities (flows) to identify bottlenecks and untapped resources.
- Stakeholder Analysis: Chart stakeholders’ roles, incentives, and power dynamics to anticipate resistance and align collaborative efforts.
Feedback Loops For Continuous Learning
- Real‑Time Metrics: Define key performance indicators (KPIs) that track both short‑term progress and long‑term impact.
- Closed‑Loop Reviews: Schedule regular retrospectives to analyze outcomes, update models, and adapt strategies based on emerging data.
- Adaptive Experimentation: Launch micro‑experiments, monitor results, and scale successful pilots—ensuring your innovation process remains agile and evidence‑driven.
By weaving design thinking’s empathy and prototyping, mindfulness‑driven flow techniques, and systems thinking’s holistic mapping into your innovation toolkit, you amplify creative flow at every stage. In the following section, we’ll explore collaborative and environmental catalysts—Techniques 6 through 10—that bring these advanced methods to life within teams and organizations.
Techniques 6–10: Collaborative And Environmental Catalysts For Innovation
Innovation seldom happens in isolation. Techniques 6 through 10 focus on harnessing collective intelligence and crafting environments—both physical and cultural—that magnify creative energy. From assembling diverse teams to embedding rituals that prime the mind, these strategies transform individual sparks into organizational firestorms of breakthrough ideas.
Technique 6: Building A Tribe Of Diverse Thinkers
A carefully curated network of collaborators amplifies creativity by bringing varied perspectives, skills, and experiences to the table. Technique 6 emphasizes forming and nurturing a “tribe” where psychological safety and inclusive leadership empower every voice:
Facilitating Cross‑Functional Brainstorm Sessions
- Define Clear Objectives: Communicate the problem scope and desired outcomes before gathering participants from different departments—marketing, engineering, design, and beyond.
- Rotate Roles: Assign shifting roles (facilitator, note‑taker, provocateur) to prevent hierarchy from stifling contributions.
- Use Structured Frameworks: Apply methods like “Round Robin” or “Brainwriting” to ensure balanced participation and rapid idea flow.
Inclusive Leadership To Harness Collective Creativity
- Model Vulnerability: Share your own uncertainties and failures to signal that risk‑taking is valued over perfection.
- Solicit Underrepresented Voices: Actively invite input from quieter team members or different cultural backgrounds to surface novel insights.
- Establish Feedback Rituals: Create regular forums—such as “Innovation Hours”—where every suggestion is acknowledged and explored without judgment.
Technique 7: Experimentation And Rapid Testing Culture
A culture that embraces experimentation transforms hypotheses into data‑driven insights. By instituting rapid testing protocols, teams iterate swiftly, learn from real results, and pivot before inertia sets in.
A/B Testing For Creative Experiments
- Hypothesis Definition: Frame clear, measurable assumptions—e.g., “Changing button color will boost click‑through by 15%.”
- Controlled Variations: Test one element at a time (headline, layout, feature) to isolate its impact on user behavior.
- Statistical Significance: Determine sample size and test duration upfront to ensure reliable conclusions.
Learning From Iterative Feedback
- Real‑User Feedback Loops: Solicit comments via surveys, usability tests, or analytics dashboards immediately after each experiment.
- Post‑Mortem Analysis: Convene brief “What Went Well / Even Better If” sessions to distill lessons learned and inform the next round of tests.
- Scale Or Kill Decision Points: Establish criteria for scaling successful experiments and sunsetting those that underperform.
Technique 8: Designing An Innovation‑Friendly Environment
Physical and digital spaces exert powerful cues on our cognitive states. Technique 8 guides you in optimizing environments to reduce friction, inspire curiosity, and signal that creative work is not just allowed but expected.
Physical Space Optimization For Creative Flow
- Flexible Layouts: Incorporate movable furniture—whiteboards, bean bags, modular tables—to support both focused work and spontaneous collaboration.
- Sensory Engagement: Use natural light, plants, and texture contrasts to reduce stress and stimulate sensory pathways tied to creativity.
- Dedicated Innovation Zones: Create “idea labs” stocked with prototyping tools, sketchpads, Post‑its, and tactile materials for hands‑on exploration.
Digital Tools And Platforms For Idea Management
- Collaborative Boards: Leverage platforms like Miro or Trello to centralize brainstorming artifacts, enable remote contributions, and track idea evolution.
- Knowledge Repositories: Maintain searchable databases of past experiments, case studies, and proof‑of‑concepts to prevent reinventing the wheel.
- Notification Controls: Configure “do not disturb” modes in communication tools to carve out uninterrupted innovation sprints.
Technique 9: Storytelling To Communicate Bold Innovations
A great idea only becomes transformative when it’s shared compellingly. Storytelling bridges the gap between raw concepts and enthusiastic adoption—crafting narratives that resonate emotionally and intellectually.
Crafting Compelling Innovation Narratives
- Hero’s Journey Framework: Position your team or product as the protagonist overcoming obstacles to deliver value.
- Data‑Driven Anecdotes: Weave customer success stories and metrics into your narrative to bolster credibility and relatability.
- Emotional Hooks: Start with vivid scenarios or challenges that evoke empathy and draw audiences into your solution pathway.
Visual Storytelling Techniques
- Infographics And Diagrams: Simplify complex processes into digestible visuals that accelerate comprehension and retention.
- Prototypes And Demos: Bring ideas to life with working models or animations that let stakeholders experience innovations firsthand.
- Slide Deck Design: Use consistent typography, iconography, and whitespace to guide viewers’ attention and reinforce key messages.
Technique 10: Rituals And Routines To Sustain Creative Flow
Rituals and routines act as reliable triggers for creative states. Technique 10 focuses on embedding daily and weekly habits that prime your mind for ideation, reflection, and sustained innovation output.
Morning Rituals For Mental Priming
- Intention Setting: Begin each day by writing one innovation goal—no matter how small—to focus cognitive resources on creative outcomes.
- Movement Breaks: Engage in light exercise or stretching to increase cerebral blood flow and enhance alertness.
- Brain Dump Sessions: Spend five minutes clearing your mind onto paper, reducing mental clutter and freeing up space for new ideas.
End‑Of‑Day Reflection And Journaling Practices
- Success Logs: Note your day’s wins—completed prototypes, breakthroughs, or collaborative victories—to reinforce progress and motivation.
- Challenge Insights: Record obstacles you encountered and outline next steps to address them, ensuring momentum carries into tomorrow.
- Gratitude Moments: Acknowledge team contributions and serendipitous inspirations to cultivate a positive, resilient innovation culture.
By integrating these collaborative and environmental catalysts, you create a self‑reinforcing ecosystem where creativity thrives. In the final section, we’ll translate these techniques into actionable plans—measuring impact, customizing your playbook, and overcoming inevitable blocks to keep your innovative engine roaring.
From Theory To Practice: Implementing And Sustaining Creative Flow
Bridging the gap between conceptual frameworks and real‑world breakthroughs requires deliberate action. In this final section, we’ll show you how to measure innovation impact, craft a bespoke creativity playbook, and conquer inevitable blocks and fatigue—ensuring your unstoppable creative flow transforms ideas into lasting results.
Measuring Innovation Impact And Progress
Quantifying creativity may seem paradoxical, but clear metrics illuminate which techniques drive genuine breakthroughs. By tracking both leading and lagging indicators, you’ll cultivate data‑driven momentum and continuously refine your innovation psychology.
- Leading Indicators: Monitor inputs like number of brainstorming sessions held, prototypes built, or new ideas submitted per month. These activity metrics signal whether your creative habits are on track.
- Lagging Indicators: Assess outcomes such as patent filings, product launches, or revenue generated from new features. These result metrics validate the effectiveness of your creative flow.
- Balanced Scorecard: Combine quantitative KPIs with qualitative feedback—customer satisfaction surveys, peer reviews, and post‑mortem insights—to capture both tangible and intangible innovation value.
- Regular Checkpoints: Establish weekly “innovation stand‑ups” or monthly reviews to celebrate wins, diagnose challenges, and pivot strategies before fatigue sets in.
Building A Personalized Creativity Playbook
No two innovators are identical. A customized playbook aligns your unique strengths, context, and goals with the ten timeless techniques—ensuring consistent, high‑velocity creative flow.
Selecting The Right Techniques For Your Context
- Self‑Assessment Audit: Rate your proficiency and enthusiasm for each technique—from growth mindset exercises to systems thinking. Highlight areas where you crave deeper mastery.
- Environment Match: Consider your work setting—remote, in‑office, or hybrid—and choose rituals and space optimizations that fit your daily rhythms.
- Team Alignment: If you lead a group, survey collaborators about preferred methods (e.g., mind mapping vs. SCAMPER) and co‑create a shared innovation toolkit.
Tracking Progress And Iterating On Methods
- Playbook Log: Document when and how you deployed a technique, the context, and immediate outcomes. Over time, patterns emerge that highlight your most potent creative levers.
- Iterative Refinement: Schedule quarterly retrospectives to prune underperforming methods, double down on high‑impact practices, and introduce new techniques as needed.
- Accountability Partners: Pair with a peer or mentor to review each other’s playbooks, exchange insights, and maintain momentum through mutual support.
Overcoming Creative Blocks And Innovation Fatigue
Even the most disciplined innovators encounter plateaus. Proactively addressing creative blocks and burnout preserves your forward momentum and keeps your psychology of innovation sharply tuned.
- Micro‑Break Interruptions: When stuck, step away for a five‑minute walk, quick stretch, or sensory reset to reenergize neural circuits and return with fresh perspective.
- Technique Rotation: Alternate between divergent and convergent exercises—e.g., switch from SCAMPER ideation to rapid prototyping—to reengage different cognitive networks and prevent monotony.
- Creative Sabbaticals: Plan mini‑retreats or deep‑work days every quarter to dive deeply into passion projects without operational distractions.
- Peer Coaching: Engage in short “design jams” or peer feedback circles to externalize your block, gain new viewpoints, and reignite inspiration.
- Well‑Being Practices: Prioritize sleep, nutrition, and mindfulness to maintain neurochemical balance—foundational to sustaining high‑velocity creative flow.
By measuring impact, curating a personalized playbook, and proactively mitigating creative fatigue, you anchor the psychology of innovation in everyday practice. Your relentless creative flow now has the structure, metrics, and resilience needed to transform ideas into enduring breakthroughs.
Discover more from Alchem Learning
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.